IP Video Conference Service Quality Technology Based on H.323 Protocol
In recent years, the H.323-based IP video conference system has been greatly developed, and already has the conditions for public operation, and to achieve this condition, service quality is the key. This article gives the service quality technology of IP video conference from two levels: network level and service level.
Keywords: H.323; IP video conference; Qos
1 Introduction
In 2001, major domestic operators set their sights on the construction of IP video conference systems. Due to the immaturity of the H.323 protocol itself, this brings certain difficulties to the public operation of IP video conferences. The public operation of IP video conferences must solve problems such as user management, service management, billing management, and video exchange interoperability. Since the Internet is a connectionless network, only one kind of bearer service-best effort service is provided. In other words, the network does not guarantee the required bandwidth to the application data stream, nor does it guarantee the quality indicators such as the transmission delay and loss rate of the data stream. For non-real-time services such as data services, best-effort delivery can meet the requirements, but for real-time communication applications such as audio or video, the network must be able to support end-to-end bearer services with a certain QoS. How to improve real-time performance and ensure the QoS of communication is the key technical requirement of the IP video system and a technical difficulty. In IP video conferencing, the QoS strategy can be implemented in two levels: the network level and the service level. This paper analyzes the QoS strategy of IP bearer network suitable for video conference and the QoS implementation of H.323 protocol from these two levels, and proposes the implementation technology of QoS for IP video conference.
2 Methods to ensure QoS of video system
There are two ways to ensure the QoS of IP video systems on the Internet.
2.1 Overengineering
That is, reserve enough bandwidth during network planning so that acceptable QoS can be obtained at any time. This method is very simple and does not require resource reservation protocols and admission control functions, but requires the deployment of enough routers and high-speed links to ensure that there is sufficient margin for network resources even when busy. It can be used in situations where the network resources are cheap and the maximum traffic of the network can be predicted.
2.2 Integrated service Internet method
Defined by the IETF Integrated Services (IntServ) working group. It needs to define a resource reservation protocol for call admission control functions, such as RSVP. Using RSVP messages, the endpoint application can propose network resources (such as bandwidth, buffer size, etc.) that must be reserved throughout the data transmission, and also determine the transmission scheduling strategy of each router along the way, thereby allowing the QoS of each data stream Control in turn.
3 Guarantee of QoS in network design
3.1 Network structure
The metropolitan area IP network is usually composed of a core layer, a junction layer, and an access layer. Each node of the junction layer is connected to the core layer through a high-speed link. In the metropolitan area IP network, consider the number of routing hops on the router connection to ensure that the number of communication routing hops between any two nodes on the network is up to 4 hops. Configure high-performance routers. The delay of a data packet after a hop is generally 10ms. This value is not determined by the length of the line and the performance of the router (for routers above 7500), so the normal delay of the data packet in the backbone network is about 50ms. From this perspective, the delay problem is not the main problem affecting the quality of IP video services.
3.2 Routing oscillation problem
There are two reasons for route oscillation.
One is the route change caused by the change of the link state. If IS-IS or OSPF is used for route discovery, the problem depends on the detection of Hello packets. At the same time, the detection is not enough, and it needs to be detected several times. Generally, it takes a few seconds to several tens of seconds from link interruption to new route selection. Such a problem occurs on the backbone network and will greatly affect the quality of real-time multimedia services. This problem is mainly solved by using the MPLS FRR capability. protection.
Another route oscillation problem is mainly caused by inadequate network design. For a large number of equal value routing or a large number of Route ReLookup or routing status update oscillation, the main solution to prevent the problem is to require all traffic when designing the network Both direction and routing need to be clearly checked by the monitor.
3.3 Dealing with oscillation problems
Oscillation is a very difficult problem to solve. Due to the problem of router principle (relative to the switch), there is always some time that may be busy, which may increase the delay of a single router to more than 100ms, which will As a result, the quality of the multimedia conference system is reduced. This situation is sometimes not necessarily caused by too much traffic on the line, and it may happen at 20% to 30% of the bandwidth. This kind of problem is mainly caused by the problem of router Buffer setting. The improvement plan is to optimize the Buffer setting of the router specifically for the conference system, but it may cause the efficiency of traditional IP services to decrease. The best case is to use two networks to provide services separately, there is a decision problem.
3.4 Network congestion
In addition to oscillation, network congestion also has a significant impact on IP video conferencing services. Therefore, when designing the network, we must prevent the occurrence of network congestion. When deploying congestion management, use the following steps:
(1) Determine whether the WAN is congested.
(2) Decide the goal according to the type of communication to be managed, the topology of the network and the design plan. When determining what kind of results need to be achieved, consider whether the goal is within several criteria:
· Able to establish a fair bandwidth allocation method for all the determined communication types;
· For communications sent from IP video services, strict priorities can be specified. This may harm the interests of communications services that are also supported but not urgent;
· Ability to customize bandwidth allocation in order to share network resources among all the applications served. Each application has specific and determined bandwidth requirements.
(3) Configure the interface with the selected queuing strategy and observe the results.
4 Realization of QoS of IP video service itself
How to improve real-time performance and ensure the QoS of communication is the key technical requirement of IP video conference. At this point, the H.323-based video conference system uses the real-time protocol and network technology proposed by the IETF. First of all, the voice signal uses the real-time transmission protocol RTP package transmission. However, RTP itself does not provide any mechanism to guarantee QoS. To ensure real-time communication, the IP network itself needs to have enhanced capabilities in this respect.
4. 1 RTP function and design ideas
The RTP protocol provides end-to-end delivery services for real-time data such as audio and video. It can transmit the timing and sequence information necessary to restore real-time signals to the receiving endpoint, and provide QoS monitoring methods to both the sender and receiver and the network operator, reducing network bandwidth Demand. RTP can greatly reduce your bandwidth usage. RTP can also tolerate a small amount of packet loss in the video conference to avoid the delay caused by data packet retransmission. RTP actually includes two protocols.
(1) RTP itself: used to transmit real-time data. Its function provides payload type indication, data packet sequence number, data transmission time stamp and data source identification.
(2) RTCP: used to transmit quality parameters for real-time signal transmission and provide a QoS monitoring mechanism; at the same time, it can also transmit the information of participants in conference communication to a "relaxed" conference without explicit member control and call establishment Communication provides a control mechanism.
The H.323 protocol uses SR and RR packets of RTCP to monitor QoS.
SR: Mainly used for multiple RTP streams, such as synchronization between audio and video, and is closely related to H.225.0. The fields related to stream synchronization are RTP timestamp and NTP timestamp.
RR: User monitoring QoS indicators, including long-term indicators and short-term indicators. If the packet loss rate is higher than the set value, the media rate should be reduced. If the receiving report interval exceeds the set value, the loss rate field in the RR packet should be used to determine whether the network is severely blocked. If so, the media rate should be reduced. If the delay jitter value of three consecutive received reports increases, the sender should take measures.
There are also messages for measuring round-trip delay in H.245: "round-trip delay request" and "round-trip delay response". This message does not contain time parameters. The request sender obtains the round-trip delay according to the difference between the sending and receiving time of the two messages. The delay is the sum of propagation delay, queuing delay at the receiving end, and processing delay. RTCP calculates the propagation delay based on the SR and RR messages, which directly reflects the QoS transmitted by the network. Therefore, the two monitor different physical quantities and do not conflict with each other.
4. 2 Verification of specific QoS measures
In order to maintain a certain quality of service, H.323 terminals take certain measures when the QoS index decreases. In fact, these measures are not to maintain the original Qos, but to reduce the quality of various media in a certain order, so that under a given bandwidth and load conditions can still provide users with acceptable services. The first thing to consider to reduce the quality is the video signal, then the data, audio and control signals in turn. Measures can be divided into two categories: short-term response and long-term response. The former aims to solve the short-term problem of short-term packet loss and increased delay; the latter is used for the increasingly serious network congestion.
(1) Dynamically adjust the image bandwidth
People's sensitivity to images and speech is different. When the image stream is delayed or jittered, the decoded image will show bit errors and dropped frames; when the speech stream is delayed or jittered, the sound will be interrupted after decoding. From the human sense, the error code of the image is more tolerant.
To improve QoS, RTP / RTCP reports can be used to obtain information about network conditions, such as packet loss rate, packet jitter, and delay, and dynamically adjust the image bandwidth based on this information. When the network condition is not good, you can notify the encoder to reduce the image bandwidth and give priority to ensuring the sound bandwidth; when the network condition is good, notify the encoder to increase the image bandwidth.
(2) Lip synchronization
Receiver: For the synchronization of the receiver's voice and image, after the terminal receives the voice and image data, it is placed in the voice buffer and the image buffer, and the voice packet is regularly taken out of the voice buffer for decoding. If they match, the corresponding image packet is decoded. The advantage of this is to consider the sensitivity of speech.
Sender: time stamp. The sender should time stamp the data packet, on the one hand the time stamp of the data packet (RTP packet) and on the other hand the time stamp of the data control packet (RTCP packet).
5 Conclusion
According to the current indications, the H.323-based IP video conference system will become a value-added service with great potential for broadband IP networks. And its ultimate goal is to operate the public so that thousands of households can enjoy video services. However, the public operation of the IP video conference system involves many issues. Service quality is the key to the implementation of IP video conferences. Therefore, in the design of IP video systems, the design of service quality should be unified. Because IP video conferencing is an emerging technology, it is still in development, and many technologies need to be further studied and discussed.
Led Emergency Driver tube is more suitable for installation in the lamp tube , slender shape with stainless steel shell . The hardness of the stainless steel case is high , which can more effectively protect the Emergency Conversion Kit circuit board and battery . The emergency power backup with multiple protection function is equipped with a recyclable rechargeable lithium ion battery , so that its service life is longer .
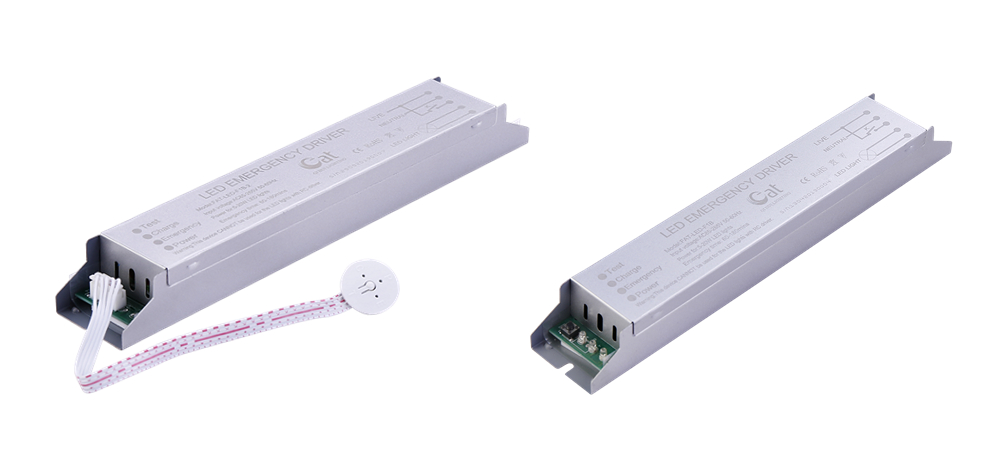
Stainless Steel Emergency Driver
Emergency Light Driver,Led Emergency Light Kit,Emergency Conversion Kit,Led Emergency Backup Lighting Kit
Jiangmen City Pengjiang District Qihui Lighting Electrical Appliances Co., Ltd , https://www.qihuilights.com